How to Read the Resistnace of a Resistor
Contents
- 1 How is the Resistance Measured?
- 2 Resistance Measurement Methods
- 3 How to measure Low Resistance (<1Ω)
- 3.one Potentiometer method
- iii.2 Voltmeter – Ammeter method
- 3.3 Kelvin Bridge
- 4 Medium Resistance Measurement (1Ω -100KΩ)
- 4.ane Ammeter Voltmeter
- 4.2 Wheatstone Span
- 4.3 Resistance Measurement Using Ohmmeter
- five High Resistance Measurement (>100KΩ)
- 5.1 Loss of accuse method
- 5.two Megger Circuit
- 6 Megaohm Bridge method
- 7 Difficulties in reading resistance
How is the Resistance Measured?
To measure an electrical resistance (Low resistance, Medium resistance, and High resistance) electronic instruments utilise two measurement techniques. They are abiding voltage and constant current.
The constant voltage method measures loftier resistance which passes a known voltage to determine electric current across unknown resistance. This method is efficient than a abiding current method as we can apply various exam voltages to find out unknown resistance.
Whereas, the constant electric current method passes a known electric current to a resistance which is non known. From this, the voltage is measured. To mensurate high resistance(200MΩ), nosotros can use the constant current technique. Digital Multimeters (DMM) use this blazon of implementation.
Now, let'southward discuss how to measure resistance.
Resistance Measurement Methods
Measuring resistance helps to know the maximum values for resistance elements such as Manganin, Copper, Nickel, etc. The resistance readings range from few microohms to several megaohms.
We tin can connect voltmeter and ammeter in a circuit to determine low resistance and high resistance in a circuit. They are a bridge method and fall of potential.
The span connection method uses a Galvanometer and a unproblematic resistor with high precision. Some of the span blazon resistance measurements are Wheatstone bridge, Air-conditioning impedance, and Kelvin double bridge.
The fall of potential method uses voltmeter and ammeter for resistance measurement. The voltmeter calculates the voltage and ammeter measures the current. From the ohms law, nosotros tin can evaluate the resistance.
How to measure Depression Resistance (<1Ω)
Low resistance is plant in switches, copper windings, transformer windings, excursion breaker contacts, bombardment strap connections, motor windings, etc.
To understand how to brand a low resistance measurement less than 1Ω, three methods are used. They are potentiometer, voltmeter-ammeter, and kelvin bridge.
Potentiometer method
The DC potentiometer method measures the unknown resistance by taking stock-still or standard resistance equally a reference value. A rheostat changes the resistance and controls the current 'I' in the circuit. An ammeter is continued in series with the unknown and standard resistance.
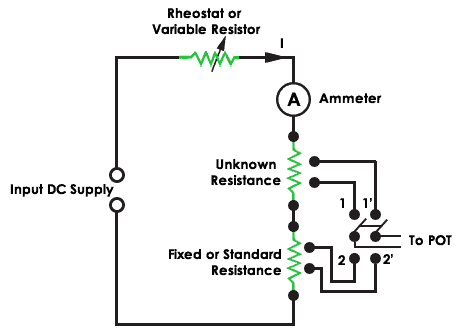
Resistance measurement using Potentiometer
When DPT switch is at position 1, information technology controls the unknown resistance and when it is at position 2 it controls the standard resistance. The voltage driblet across the resistance is taken as output using ohms law. Hence the unknown resistance is given past
Unknown resistance = (Voltage drib across Unknown resistance/Voltage drop across Standard resistance) * Standard resistance
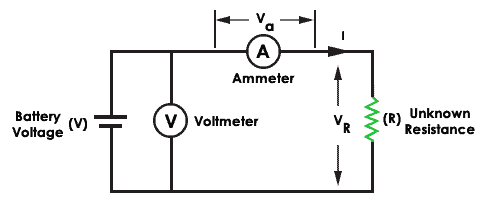
Voltmeter – Ammeter method
The voltmeter – Ammeter method measures the low resistance with an accuracy of ±ane%. To achieve i pct tolerance, it uses four terminals for measurement. Two of them are current terminals (C1, C2), and the remaining 2 are potential terminals (V1, V2).
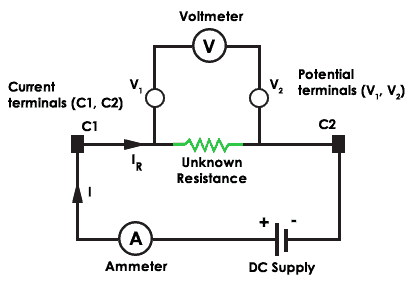
Voltmeter – Ammeter method
There will a less voltage driblet across potential terminals and the current flows in and out from the unknown resistor. The contact resistance is small at the current terminals and the unknown resistance is calculated from the voltage drop across voltmeter and electric current through the ammeter.
Kelvin Bridge
The Kelvin bridge (Thomson Bridge) measurement has the benefit of canceling the actress resistances from the test leads and contacts. The below figure shows the kelvin double bridge circuit.
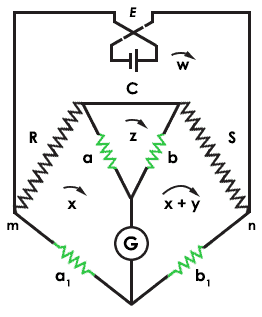
Kelvin Bridge
The span uses double ratio arms to nullify the resistance. 'R' is the unknown resistance and 'S' is the standard resistances of depression value. 'C' is a heavy copper connection. The branches a, b, a1, and b1 are high resistances values when compared with 'R' and 'South'.
The kelvin double bridge equation is given by the formula
R/South = (a1/b1) – {C/Southward × (b/(a+b+C)) × (a1/b1 – a/b)}
For right measurement, the ratio of 'R', 'Southward', and a, b must be equal. Now, the excursion is in residue condition. This will deflect the current in Galvanometer 'G'. This span measures the resistances in the range from 0.one ohms to one ohm.
Medium Resistance Measurement (1Ω -100KΩ)
Ammeter Voltmeter
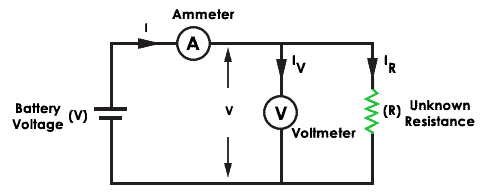
The Ammeter-Voltmeter method works using two configurations. In the beginning setup, connect the ammeter in series with the unknown resistance. This method measures the right value of the current through the unknown resistance 'R'.
The voltmeter equals the sum of the current across ammeter and voltage beyond resistance 'R'. To measure resistance output (Rm ), the value of resistance 'R' must be greater than the resistance of ammeter (Ra ). Hence this method is suitable for measuring medium resistances.
The true value of measured resistance is Rm = R+Ra . To get exact resistance, the ammeter resistance must be zero. This is truthful in the platonic case.
In the second configuration, connect the voltmeter in parallel with the unknown resistance. The voltmeter measures the correct voltage. But here the ammeter measures the sum of the currents flowing through the voltmeter and unknown resistor. In the platonic case, the voltmeter resistance is infinite to get truthful voltage output.
The error at total scale for the ammeter voltmeter method is virtually 0 to 1%. Hence the Wheatstone bridge is preferable.
Wheatstone Span
The Wheatstone bridge is an old method and is no longer in practise. Merely it tells the concept of a balanced bridge to measure unknown resistance. The span has diamond shape grouping which consists of four resistances A, B, R, and South. The resistance B and S are fixed resistances.
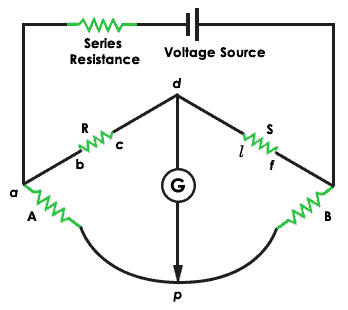
Wheatstone Span
The voltage is applied to the input terminals 'a' and 's' and the galvanometer (likewise known as a goose egg detector) is connected to the output terminals 'p' and 'd'. To measure the resistance 'R' using Wheatstone bridge vary the standard resistance 'A' until the current in the galvanometer reads zero current reading. This proves that the bridge is present in a counterbalanced condition.
Resistance Measurement Using Ohmmeter
Here are steps on how does ohmmeter piece of work to measure the resistance of a resistor or some component.
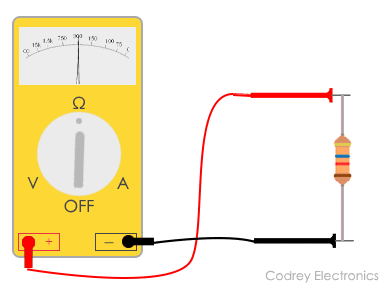
Measuring resistance using an ohmmeter
- The first important step is to practise is turning off the circuit (To ensure the accuracy in measurement and not to damage the excursion, disconnect the power to the circuit)
- Identify the probes on the respective sockets:
- Insert the black probe to the mutual (COM) port of the multimeter
- Insert the red probe to the voltage (VmAΩ) port of the multimeter (Red terminal)
- Aught the meter by placing the 2 probes touching together and adjust the punch or knob by turning it until it shows zero ohms
- Test the resistance of the component using the two probes by placing at each side
- Turn the knob to the relevant ohms range yous are trying to measure out. (If the pointer deflects to the correct side of the scale, subtract the range to one level. If the pointer deflects to the left side of the scale, increase the range to ane level)
- Have the reading on the scale and multiply it with the appropriate range on the punch.
- Make the ohmmeter cipher again before testing another component.
Annotation: Ever cheque for the resistances connected in parallel. The multimeter computes the resistance between the dissimilar paths in a circuit.
The multimeter measures the total resistance in a circuit through all possible paths. It's always improve to remove the component to measure the resistance. Otherwise, the multimeter will evidence wrong resistance reading.
High Resistance Measurement (>100KΩ)
Loss of charge method
The resistance measurement by using the loss of charge method uses an unknown resistance (R) in parallel with the voltmeter and a capacitor (C). When applying the DC voltage, the current flows through the circuit and the capacitor charges until the battery voltage. Subsequently that, it discharges through the resistance 'R'.
The equation for voltage across the capacitor is 5 = Five.e(-t/CR)
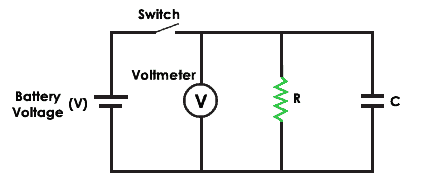
The resistance equation 'R' is equal to 0.4343t/ (C log10 V/(V-eastward))
Megger Excursion
The use of megger is to measure high insulation resistance in a circuit. The below effigy shows the circuit of megger. It uses a hand-driven generator which produces a voltage of 500V, 1000 and 2500V.
The generator incorporates an automatic clutch that uses the centrifugal principle to operate the instrument. The generator supplies a abiding voltage to measure the depression insulation resistance.
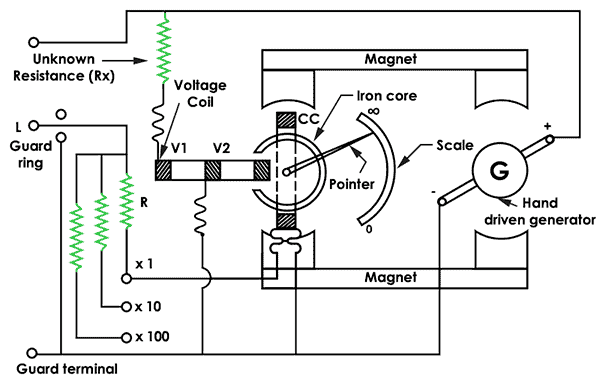
The megger has three coils (2 voltage coils and 1 current coil). The current coil moves in the clockwise path and the voltage coils in the counterclockwise. The two coils make the arrow set it to the middle position. At present, y'all can apply the voltage and measure the resistance.
The arrow calibration becomes steady by connecting a resistance under exam (Unknown resistance Rx).
Megaohm Bridge method
The megaohm bridge measures high resistance from 0.1 megaohms to 1 megaohm. The baby-sit terminal is continued to the galvanometer (G). The multiplier switch is used to select the range of resistances to be measured.
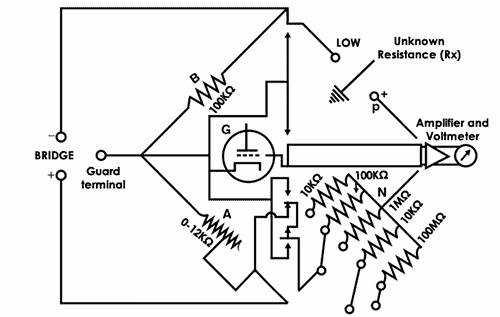
A fixed resistance of 100 KΩ and connecting a guard concluding to a guard excursion removes the leakage resistance.
Difficulties in reading resistance
- The human trunk absorbs current, hence make certain to avert contact with the component when measuring with multimeter or ohmmeter.
- Test the components individually to get correct resistance.
- Don't measure out the resistance in a power-on excursion. This will requite incorrect readings.
Tip: Power off the excursion and measure the resistance.
- Bank check the harm of the component (shows cipher resistance in multimeter).
- Repeatability to measure depression resistance within a few micro ohms. This will impact the electric current consumption in an electric circuit.
Determination
Present, there are multiple methods for resistance measurement. Amid them, LCR meter and digital low resistance ohmmeters replace with the Wheatstone bridge, Kelvin double bridge, and other methods. Hence it is necessary to select a proper instrument for testing the resistance.
Source: https://www.codrey.com/electrical/how-to-measure-resistance/
0 Response to "How to Read the Resistnace of a Resistor"
Post a Comment